How Can Blockchain Be Considered as a Decentralized System from a Logical Perspective?

Decentralization is the dispersing of control and decision-making functions away from a centralized entity or authority in the blockchain. There is no longer a third party such as an individual, organization, or group. An authority does not control blockchains; instead, the entire network of participants governs the system. This concept is key to understanding the different types of blockchains and how they achieve decentralization.
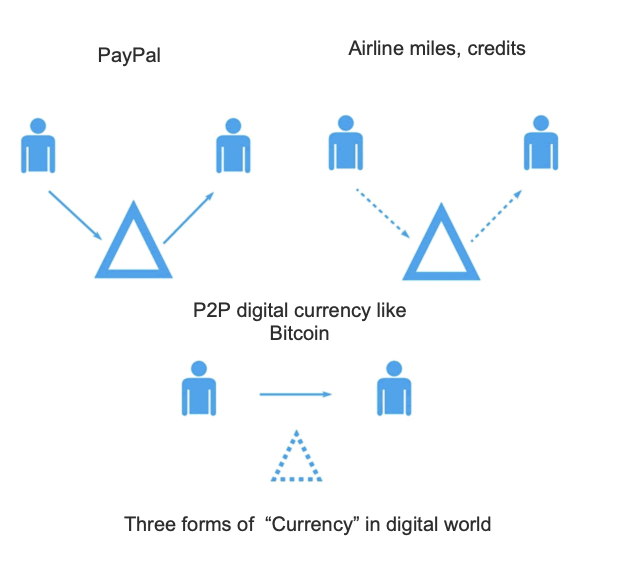
Blockchain achieves decentralization through multiple interconnected mechanisms that work together to create a trustless and distributed system.
Network Architecture
The blockchain operates on a distributed network where each node maintains a copy of the ledger, eliminating single points of control [1]. This peer-to-peer structure ensures that no single entity has complete authority over the network’s operations or data.
Consensus Mechanisms
Validation Process
The network reaches agreement through consensus protocols where multiple nodes must validate and verify transactions. This collective decision-making process ensures:
- Transaction legitimacy
- Network-wide agreement on the blockchain state
- Protection against fraudulent activities
Security Features
The consensus system provides robust security through:
- Multiple node validation requirements
- Cryptographic verification
- Immutable transaction records [2]
Types of Decentralization
Physical Decentralization
Nodes are geographically distributed across various locations, enhancing network resilience and reducing the risk of localized failures.
Transactional Decentralization
Transaction processing power is distributed across multiple nodes, preventing any single node from controlling or manipulating the process. This allows for direct peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries, such as in the case of smart contracts.
Network Governance
The blockchain maintains decentralization through:
- Open-source protocols ensuring uniform capabilities
- Interdependent node relationships
- Automated updates and synchronization [6]
Data Management
Distributed Ledger
Each node in the network:
- Stores a complete copy of the blockchain
- Participates in transaction verification
- Updates simultaneously with new transactions [1]
This distributed approach ensures that the network remains decentralized while maintaining data integrity and security across all participating nodes.
Table 1: Issuance Type and Transaction Characteristics
| Cash | Digital Currency | Reward Points | Decentralized Digital Currency | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Issuance type: | Centralized | Centralized | Centralized | Decentralized |
| Transaction: | Decentralized | Centralized | Centralized | Decentralized |
Table 2: Real-World Mapping and Automatic Issuance
| Cash | Digital Currency | Reward Points | Decentralized Digital Currency | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Is it mapped to real-world currency: | / | Yes | No | No |
| Is it automatic issuance: | / | No | Yes | Yes |
If you are interested in learning more about how cryptocurrencies operate, check out our detailed guide on the best cryptocurrency payment gateways for e-commerce.

